After two release candidates, the Blender Foundation has now released
Blender 2.70
New features include initial support for volumetrics in Cycles, and
faster rendering of hair and textures. The motion tracker now supports
weighted tracks and has improved planar tracking. For mesh modeling
there are new Laplacian deform and wireframe modifiers, along with more
control in the bevel tool. The game engine now supports object levels of
detail.
The first results from the new user interface project are also in
this release, with dozens of changes to make the interface more
consistent and powerful. This is also the first release of the
multithreaded dependency graph, which makes modifier and constraint
evaluation faster in scenes with multiple objects.
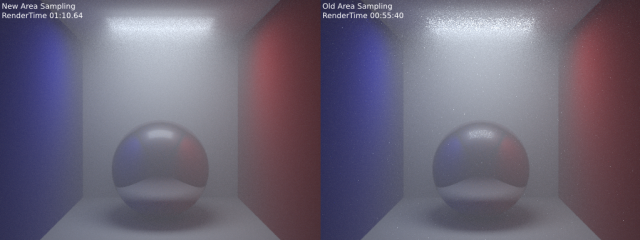
Cycles now has initial support for volume rendering including
emission, absorption and scattering. Volume rendering can be used to
render effects like fire, smoke, mist, absorption in glass, and many
other effects that can't be represented by surface meshes alone.
CPU rendering performance was improved, particularly for hair, textures and Open Shading Language.
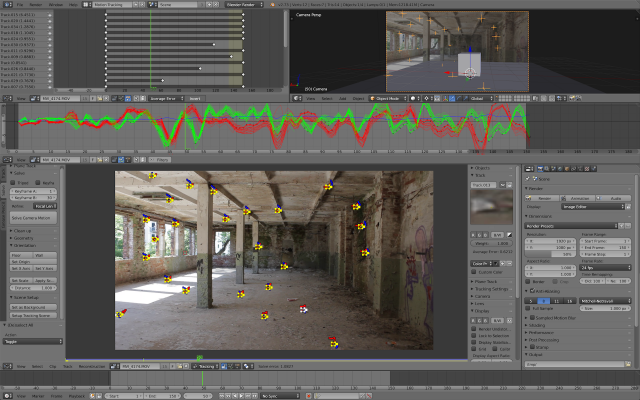
Trackers can now be weighted, to keep the result stable as feature
disappear or become difficult to track. The plane track workflow was
improved to be easier to control. Automatic feature detection was made
more robust using a new detector algorithm.
The toolbar now has tabs to organize tools in categories. Multiple
buttons can now be edited at once, for example for XYZ axes or color
channels. Transform tools now have a mode to enter expressions and
units. Other changes were done to improve lists, header menus, tooltips,
buttons, menus and more.
The Laplacian Deform modifier was added to pose a mesh while
preserving geometric details of the surface, and a new wireframe
modifier allows you transform your mesh into a wireframe representation.
The boolean modifier now supports ngons, and there are improvements to
the bevel, screw and triangulate modifiers.
The bevel tool now offers more control over the bevel profile and results, and the knife tool was improved as well.
An important change that happened under the hood is the threaded
dependency graph. This means that object modifiers and constraints,
among other things, can now be computed with multiple threads taking
advantage of multicore processors. This will be most noticeable with
scenes that have many objects, or multiple objects with heavy modifiers.
This is the first step in making the dependency graph in Blender more
powerful.
The Blender game engine now supports discrete level of detail for
meshes. For game developers, support for working with Photoshop PSD
files has been added.
A new view navigation walk mode has been added, which has a
control scheme as typically found in first person shooter games. This
can be useful for game developers to navigate levels as if in a game.
The Freestyle Python API is an essential part that makes it a highly
programmable NPR rendering engine. This API has been reorganized.
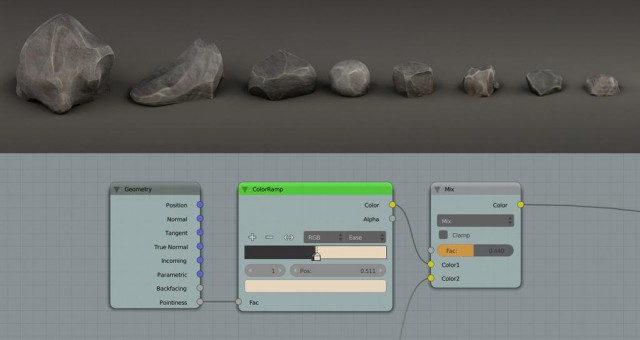
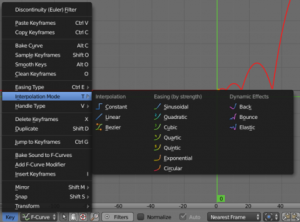
Many small changes and features were done all over Blender. Some
notable new feature are normalized display for FCurves, derivative map
baking, baking to vertex colors, better visualization of masks and
control over mask filling, gravity option for sculpting, negative
texture values to support vector displacement and a Lamp Data shading
node to create more customized NPR shaders.
Download link: http://www.blender.org/download/